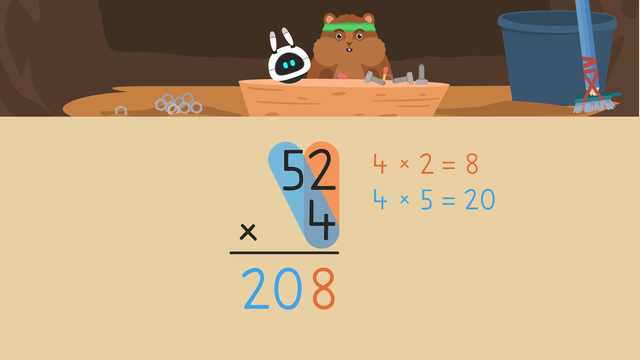Distributive Property of Multiplication


Basics on the topic Distributive Property of Multiplication
Distributive Property
What is the distributive property of multiplication? We can explain distributive property of multiplication breaking down one factor into smaller parts, to multiply the broken down parts by the other whole factor, and then adding them together to get the product of the original factor pair. To understand and apply the distributive property of multiplication, read on to see an example of distributive property.

Distributive Property – Examples
Let’s have a go at using the distributive property of multiplication! Below, we have the factor pair four and six.




Distributive Property Multiplication – Summary
To use the distributive property of multiplication, remember these steps:
| Step # | What to do |
|---|---|
| 1 | Break down one of the factor pairs |
| 2 | Distribute the whole factor to the broken down factor pairs |
| 3 | Multiply both smaller factor pairs |
| 4 | Add the product of both to find the product of the original factor pair |
After watching the video, you will find more interactive exercises for practice of distributive property and a distributive property of multiplication worksheet.
Transcript Distributive Property of Multiplication
Big 'Arry seems upset, it looks like Detective Squeaks is needed! "Big 'Arry! What seems to be the problem?" “Help! I don't know how many squares I have in total, but apparently, the Little 'Arry's can help!" Let's help Detective Squeaks calculate how much Big 'Arry has altogether by using the distributive property of multiplication. The distributive property of multiplication is sometimes called the distributive law of multiplication. It teaches us that one factor can be broken down into two smaller factors, to solve a multiplication problem by breaking down one factor, or number, into smaller parts. We can multiply them separately then add the products together to find the same product as if we had multiplied the original two factors together. The distributive property of multiplication is very useful, because it allows bigger multiplication problems to be broken down into smaller ones! Let's practise with four times six. We can set up an array to model this problem. Break down one of the factors into smaller numbers that add up to the factor. For this problem, we will break down the six into three plus three. Next, multiply each number by the factor outside the brackets, this is four. We need to find four times three, twice. We can make two arrays with four rows of three to help. Now, find the products of the two smaller factor pairs. Four times three gives a product of twelve. We can check the answer by counting the arrays. Finally, add together the products. This means we will find the sum of twelve plus twelve which is twenty-four. Let's check the answer by finding the product of the original problem! The product of the original problem is twenty-four so the answer is correct! Now we have looked at the distributive property of multiplication and how it works, let's help Detective Squeaks calculate how many squares Big 'Arry has in total! Big 'Arry is an array of seven by five, so set up an array with seven rows of five! What is the next step? Break down one of the factors! Let's break down the larger of the two factors, seven. How can we break down the seven? We can break the seven into four plus three. What is the next step? Multiply both numbers by the factor outside the brackets, which is five. What should we do next? Find the product of both! Four times five equals twenty and three times five equals fifteen! Check your work by counting the arrays. What is the next step? Add both products together! Twenty plus fifteen equals thirty-five. What is the final step? Check your answer by finding the product of the original equation. Seven times five is thirty-five, so the answer is correct! Whilst Detective Squeaks tells Big 'Arry how many squares he has in total, let's review! Remember, to use the distributive property of multiplication, first identify a factor to break down into smaller parts. Next, multiply both smaller factors by the larger factor and solve. Then, add together the two products to get the total. Finally, check your answer by finding the product of the original problem! "So Big 'Arry, you basically have as many squares as the Little 'Arry's have put together!" "Woah, what's going on here!" "Imani, you will never believe what I just saw in that virtual reality world!"
Distributive Property of Multiplication exercise
-
How can we find Big 'Arry's area?
HintsThere are two correct answers.
Break down one of the original factors into two smaller factors and multiply both of these by the other original factor. Here, 7 has been broken into 2 and 5, then both multiplied by 5.
Solve both of the calculations within the brackets. Do both products total the original caculation of 7 x 5?
SolutionThe original array was 7 x 5.
- Break down the bigger factor (7) into two parts.
- Then multiply both of these by 5.
- We could break down 7 into 2 and 5: (2 x 5) + (5 x 5). 10 + 25 = 35.
- We could break down 7 into 3 and 4: (4 x 5) + (3 x 5). 20 + 15 = 35.
-
Use the distributive law.
HintsTo find the factors that 6 can be broken into, think about what 6 is made up of.
Once you know that 6 is broken into 4 and 2, what are the next steps?
SolutionThis array has been made with 6 squares across and 5 squares down.
Instead of solving 6 x 5 we can break down the factor, 6, into 4 + 2.
Then we solve: 4 x 5 = 20 and 2 x 5 = 10.
Finally, we can add together the two products, 20 and 10 to get the total of 30.
We can check this by solving 6 x 5 which also equals 30.
-
Find the equations that match each array's area.
HintsThis array is 8 x 4. Can the 8 be broken down into two other factors?
In this array, 8 x 4 could be broken down into (5 x 4) + (3 x 4).
SolutionArray measuring 7 x 3.
- 7 can be broken into 5 and 2.
- (5 x 3) + (2 x 3) = 21.
- This is the same as 7 x 3 = 21.
Array measuring 9 x 4.
- 9 can be broken into 5 and 4.
- (5 x 4) + (4 x 4) = 36.
- This is the same as 9 x 4 = 36.
Array measuring 8 x 5.
- 8 can be broken into 5 and 3.
- (5 x 5) + (3 x 5) = 40.
- This is the same as 8 x 5 = 40.
Array measuring 9 x 5.
- 9 can be broken into 6 and 3.
- (6 x 5) + (3 x 5) = 45.
- This is the same as 9 x 5 = 45.
-
Breaking down factors.
HintsWhen there are two factors multiplied together, look at the larger factor. Can you see another equation where this factor has been split into two smaller factors?
An example of a larger factor being broken into two smaller factors would be: 15 x 7. 15 can be split into 10 + 5 to become (10 x 7) + (5 x 7).
Solution- (3 x 5) + (5 x 5) = 8 x 5. Both equations = 40
- (6 x 6) + (3 x 6) = 9 x 6. Both equations = 54
- (10 x 7) + (2 x 7) = 12 x 7. Both equations = 84
- (6 x 4) + (6 x 4) = 12 x 4. Both equations = 48
-
Finding the array to match the equation.
HintsWhat two factors can 7 be split into? Both of these are then multiplied by 3.
Solve the separate multiplication equations (5 x 3) + (2 x 3) then combine these products to find the total. This is how many squares are in the array.
7 x 3 = 21. Can you see an array with 21 squares?
Solution- This image shows how the array 7 x 3 can be broken into two parts to make the multiplication simpler.
- An array of 7 x 3 is the same as an array of 2 x 3 and 5 x 3.
- (2 x 3) = 6 and (5 x 3) = 15.
- 6 + 15 = 21.
- 7 x 3 = 21.
-
Finding factors.
HintsFirst find the equations where two factors multiply together to make the product.
Where an equation has been broken down into two parts, multiply the equations within the brackets, then add these products together.
Solution36
- (3 x 4) + (6 x 4)
- (2 x 6) + (4 x 6)
- (9 x 3) + (3 x 3)
- 9 x 4
42
- (5 x 6) + (2 x 6)
- (8 x 3) + (6 x 3)
- 7 x 6
25
- (2 x 5) + (3 x 5)
- 5 x 5
 Do you want to learn faster and more easily?
Do you want to learn faster and more easily?